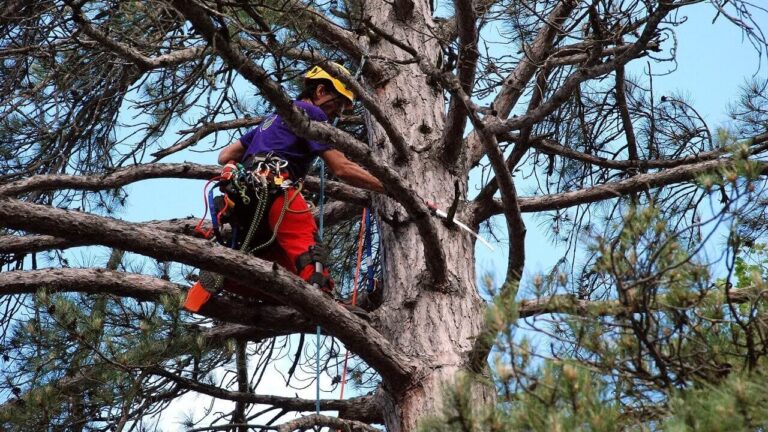
What’s Included in a Comprehensive Arborist Report Sydney?
What Is a Comprehensive Arborist Report in Sydney and Why Is It Important?
A comprehensive arborist report Sydney is a detailed professional document that evaluates the health, safety, and structural condition of trees on a property. Prepared by qualified arborists, this report provides critical insights into tree management and compliance requirements.
The importance of arborist reports extends across multiple stakeholder groups:
- Property owners rely on these assessments to understand potential liabilities and maintenance obligations associated with trees on their land.
- Developers need them to navigate council approval processes and ensure projects comply with tree preservation laws.
- Local councils use these reports to make informed decisions about development applications and protect significant vegetation.
What’s included in a comprehensive arborist report Sydney? The document typically includes:
- Tree health and condition assessment — examining vitality, disease presence, and pest infestations
- Structural integrity evaluation — identifying safety hazards and stability concerns
- Species identification — determining exact tree types for legal compliance
- Risk assessment — analyzing potential threats to people, property, and structures
- Professional recommendations — outlining required actions like pruning, treatment, or removal
- Compliance guidance — addressing local council regulations and development requirements
- Photographic evidence — supporting visual documentation of findings
- Legal documentation — formal paperwork suitable for council submissions
These reports serve as essential tools for responsible tree management. They protect property values, ensure public safety, and maintain Sydney’s urban canopy while meeting statutory obligations. The thorough nature of these assessments helps prevent costly mistakes and legal complications related to tree work.
What Qualifications Do Arborists Preparing These Reports Typically Have?
AQF Level 5 arborist certification represents the gold standard for qualified arborists Sydney property owners should seek when commissioning comprehensive reports. This nationally recognized qualification—formally known as the Diploma of Arboriculture—demonstrates advanced knowledge in tree biology, risk assessment methodologies, and Australian standards for tree management.
The certification requires extensive study covering tree physiology, identification of over 200 species, structural assessment techniques, and legal frameworks governing tree protection. Arborists holding this credential have completed rigorous practical assessments and theoretical examinations administered by registered training organizations.
Why Certification Matters for Report Quality
Certified professionals bring systematic assessment frameworks that untrained individuals cannot replicate. Their training includes standardized visual tree assessment methods, understanding of biomechanics affecting tree stability, and knowledge of pathology that might compromise structural integrity. This expertise directly translates to more accurate hazard identification and defensible recommendations.
Reports prepared by AQF Level 5 certified arborists carry greater weight with local councils during development application processes. Sydney councils frequently require reports from qualified professionals meeting specific credential thresholds, particularly for significant trees or heritage-listed specimens.
Experience Beyond Paper Credentials
Years of practical experience complement formal qualifications by exposing arborists to diverse tree conditions across Sydney’s varied microclimates and soil types. Experienced practitioners recognize subtle indicators of decline that textbooks cannot fully capture—such as species-specific stress responses or regional pest patterns affecting particular suburbs.
The combination of certification and field experience enables arborists to:
- Accurately predict tree response to proposed construction activities
- Identify early-stage diseases before visible symptoms become severe
- Provide realistic timeframes for recommended interventions
- Assess whether trees can tolerate specific environmental changes
Insurance and Professional Indemnity Requirements
Qualified arborists Sydney councils accept for formal submissions maintain professional indemnity insurance and public liability coverage. These protections matter when reports influence decisions affecting property values, public safety, or legal disputes between neighbors. Insurance providers typically require proof of relevant qualifications before extending coverage to arboricultural consultants.
Professional membership with organizations like Arboriculture Australia provides additional credibility markers. Members commit to ongoing professional development and adherence to industry codes
What Does a Tree Health and Condition Assessment Include?
A tree health assessment Sydney examines the physiological state of trees through systematic evaluation of foliage, bark, root systems, and growth patterns. Qualified arborists inspect crown density, leaf colour, and seasonal growth indicators to determine whether trees are thriving, declining, or in distress.
Evaluating Overall Tree Vitality
The assessment begins with visual inspection of the tree’s canopy. Arborists look for:
- Leaf density and distribution across the crown
- Colour variations indicating nutrient deficiencies or stress
- Seasonal growth patterns that deviate from species norms
- Dieback in branches or sections of the canopy
Bark condition reveals significant information about internal health. Cracks, splits, or unusual textures often signal underlying problems requiring immediate attention.
Identifying Disease Symptoms
Tree disease evaluation involves recognizing specific pathogens affecting Sydney’s urban forest. Common indicators include:
- Fungal fruiting bodies (mushrooms or brackets) on trunk or roots
- Cankers or lesions on bark surfaces
- Premature leaf drop or discolouration
- Powdery mildew or sooty mould on foliage
- Root rot symptoms visible at the base
Arborists document disease progression stages to recommend appropriate treatment protocols or determine if removal becomes necessary for preventing spread to neighbouring trees.
Detecting Pest Infestations
Pest infestation detection requires examining trees for insect activity and damage patterns. Sydney properties commonly face threats from:
- Psyllids causing leaf distortion and honeydew secretion
- Borers creating entry holes and sawdust accumulation
- Scale insects forming protective coverings on branches
- Termites compromising structural wood integrity
Arborists assess infestation severity by checking for active insect presence, frass deposits, and extent of tissue damage affecting the tree’s vascular system.
Assessing Structural Damage
Physical damage assessment identifies wounds, cavities, and decay that compromise tree vitality. Inspection covers:
- Storm damage from broken branches or split trunks
How Is Structural Integrity and Safety Evaluated in the Report?
A tree structural integrity assessment examines the physical stability of trees to identify immediate and potential hazards. Arborists conduct detailed visual inspections and sometimes use specialized equipment to detect internal decay, cracks, weak branch unions, and root system problems that compromise stability.
Assessing Potential Hazards
The tree safety inspection Sydney process focuses on identifying specific threats that trees pose to their surroundings. Arborists evaluate:
- Overhanging branches positioned above structures, walkways, or parking areas
- Dead or dying limbs that could detach without warning
- Leaning trunks indicating root failure or soil movement
- Split or cracked stems showing advanced structural failure
- Co-dominant stems with weak unions prone to splitting
- Root plate lifting suggesting imminent tree failure
Each identified hazard receives a risk rating based on the likelihood of failure and potential consequences. Trees near high-traffic areas or valuable property receive closer scrutiny than those in isolated locations.
Methods Used to Determine Structural Soundness
Qualified arborists employ multiple techniques during hazard identification:
Visual Inspection Techniques
- Examining bark for wounds, cavities, or fungal fruiting bodies
- Checking branch attachment points for included bark or weak unions
- Observing crown architecture for imbalanced weight distribution
- Assessing root collar for signs of decay or girdling roots
Advanced Assessment Tools
- Resistograph testing to measure internal wood density
- Sonic tomography to map decay patterns within the trunk
- Root collar excavation to expose hidden structural problems
- Pull testing to evaluate root anchorage strength
The arborist documents findings with precise measurements, noting cavity depths, crack lengths, and lean angles. This quantitative data supports professional judgments about tree stability.
Safety Considerations for People and Property
The evaluation prioritizes human safety and property protection above all other factors. Arborists consider the tree’s proximity to:
- Residential buildings and commercial structures
- Public footpaths and roadways
- Children’s play areas and schools
- Power lines and utility infrastructure
- Fences
Why Is Species Identification Important in Arborist Reports?
Accurate tree species identification determines whether a tree falls under legal protection and directly affects what actions property owners can legally take. An arborist must correctly identify each tree’s botanical name because misidentification can lead to illegal removal, substantial fines, and project delays.
Protected tree species receive special status under state environmental legislation and local council development control plans. Trees like the Turpentine (Syncarpia glomulifera), Blackbutt (Eucalyptus pilularis), and certain fig species cannot be removed or significantly pruned without specific approvals. Sydney councils maintain registers of significant trees, and species identification confirms whether a tree appears on these protected lists.
Development applications require precise species information because approval conditions vary dramatically between common and protected species. A developer planning to remove a Spotted Gum (Corymbia maculata) faces different regulatory requirements than someone dealing with an introduced species like a Camphor Laurel (Cinnamomum camphora). The species name appears throughout council documentation, environmental impact statements, and legal permits.
Species identification also reveals growth characteristics that inform management decisions. Native species like Angophoras develop hollow limbs as they age, creating habitat value that may trigger additional preservation requirements. Introduced species might be classified as environmental weeds, potentially simplifying removal approvals while requiring specific disposal methods to prevent spread.
Arborists use multiple identification methods including:
- Leaf shape, size, and arrangement patterns
- Bark texture and colour characteristics
- Flower and fruit structures when present
- Growth habit and branching patterns
- Historical records and site context
The species information connects to broader ecological assessments. A property containing multiple specimens of threatened species may require biodiversity offset calculations before development proceeds. Heritage-listed species or trees of cultural significance to Indigenous communities trigger consultation requirements that wouldn’t apply to common ornamental plantings.
Insurance and liability considerations depend on accurate species identification. Certain species like eucalypts are known for sudden limb drop, affecting risk assessments and recommended management strategies. Species-specific disease susceptibilities help predict future health issues and inform long-term maintenance planning.
What Recommendations Are Typically Provided by Arborists?
Arborists provide actionable recommendations tailored to each tree’s specific condition and circumstances. These expert suggestions form the practical core of the report, guiding property owners toward appropriate management decisions.
Professional Advice on Pruning and Removal
Tree pruning advice Sydney arborists offer addresses both structural and health concerns. Recommendations specify which branches require removal, the optimal pruning technique (such as crown thinning, crown lifting, or deadwood removal), and the best timing for the work. When trees pose unacceptable risks or have deteriorated beyond recovery, arborists provide clear tree removal recommendations with justification based on safety assessments and structural analysis.
Pruning suggestions often include:
- Removal of deadwood exceeding certain diameters
- Clearance pruning to maintain safe distances from buildings or powerlines
- Formative pruning for young trees to establish proper structure
- Weight reduction for overextended limbs
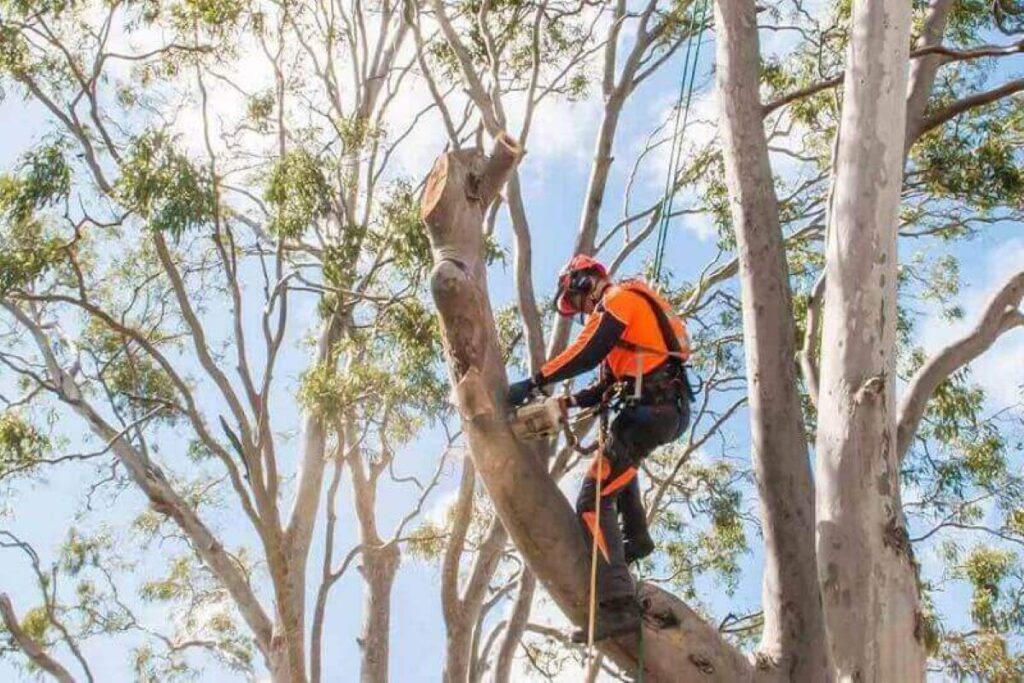

Treatment Options for Diseases and Pests
When inspections reveal health issues, arborists detail specific interventions. Pest treatment suggestions might include targeted insecticide applications for borers, scale insects, or psyllids affecting particular species. Disease management recommendations range from fungicide treatments for leaf spot diseases to soil amendments addressing root health problems.
Treatment plans typically specify:
- The exact products or methods suitable for the identified issue
- Application timing and frequency for maximum effectiveness
- Whether treatments require licensed pest control operators
- Expected recovery timeframes and success rates
Ongoing Maintenance Strategies
Long-term care recommendations ensure trees remain healthy assets rather than developing into liabilities. Arborists prescribe regular inspection intervals—often annually or bi-annually depending on tree condition and risk factors. Maintenance schedules might include periodic mulching, appropriate watering during establishment or drought, and monitoring for emerging pest or disease issues.
Preventative strategies address:
- Soil improvement through organic matter incorporation or aeration
- Protection zones around root systems during construction activities
- Appropriate fertilization regimes based on soil testing results
- Monitoring protocols for trees with identified but manageable concerns
These recommendations balance tree preservation with safety requirements, providing property owners with clear pathways for responsible tree management that satisfies both regulatory obligations
How Does the Report Address Compliance with Local Regulations?
A comprehensive arborist report serves as a critical compliance document that interprets and applies council regulations Sydney to your specific property situation. The report explicitly references relevant local council tree preservation orders, development control plans, and any specific tree protection legislation applicable to your area, translating complex legal requirements into actionable guidance for property owners.
Key Regulatory Information Included:
- Identification of trees protected under local environmental plans
- Specific council requirements for tree work permissions NSW
- Applicable tree preservation orders affecting the property
- Heritage tree listings and their associated restrictions
- Vegetation management overlays and their implications
The arborist evaluates whether proposed works require formal approval from your local council, detailing the specific application processes needed. For trees exceeding certain size thresholds or belonging to protected species, the report outlines the exact development application requirements, including which forms must be submitted, what supporting documentation is necessary, and the typical approval timelines property owners should expect.
When development applications involving trees are required, the report provides comprehensive technical data formatted to meet council specifications. This includes tree location plans with accurate measurements, trunk diameter calculations using standardized methods, canopy spread dimensions, and detailed species information—all presented in the format councils require for processing applications efficiently.
Compliance Documentation Features:
- Tree protection zone calculations based on Australian Standards
- Structural root zone assessments for construction projects
- Impact statements for proposed development near trees
- Mitigation measures to satisfy council conditions
The report addresses legal compliance during tree management activities by clearly stating which works can proceed without approval and which require permits. This distinction prevents costly violations of local tree protection laws, which can result in substantial fines ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on the severity of the breach and the significance of the affected tree.
For properties in bushfire-prone areas, the report reconciles competing requirements between asset protection zones and tree preservation regulations. Arborists provide specific guidance on how to achieve necessary bushfire safety clearances while maintaining compliance with vegetation protection rules, often recommending strategic pruning approaches that satisfy both objectives.
The document includes references to relevant sections of the Environmental Planning and Assessment Act 1979 and local council development control plans, providing property owners with the legal framework supporting the arborist’s recommendations. This legislative context helps stakeholders understand not only their obligations but also the rationale behind certain decisions made in relation to tree management practices on their land.
What Role Does Photographic Evidence Play in the Report?
Photographic evidence in an arborist report serves as critical visual proof of the arborist’s observations and findings. High-quality images capture the current state of trees at the time of inspection, providing an objective record that supports written assessments and recommendations.
Components of Visual Documentation
The components of visual documentation for trees in Sydney typically include:
- Close-up shots of disease symptoms, pest damage, or decay
- Wide-angle views showing tree structure and surrounding context
- Images of structural defects like cracks, splits, or cavities
- Photographs documenting proximity to buildings, power lines, or other infrastructure
- Before-and-after images when follow-up inspections occur
Images eliminate ambiguity in written descriptions. A photograph showing the extent of root plate damage or the severity of canopy dieback communicates information far more effectively than text alone. Council officers reviewing development applications can see exactly what the arborist observed without visiting the site themselves.
The credibility of findings increases substantially when backed by clear visual evidence. Photographs timestamp the tree’s condition, creating an indisputable record that protects both property owners and arborists from potential disputes. If a tree’s health deteriorates rapidly or a structural failure occurs, dated images establish the baseline condition at assessment time.
Council submissions benefit enormously from comprehensive photographic documentation. Local authorities require visual proof when assessing applications for tree removal or significant pruning works. Images showing hazardous conditions, irreversible decline, or conflicts with proposed development strengthen applications and expedite approval processes.
Legal proceedings involving tree disputes rely heavily on photographic evidence. Property damage claims, neighbour disputes, or compliance enforcement cases all require objective documentation. Professional-quality images with proper labeling and context notes provide compelling evidence that written reports alone cannot match.
Annotated photographs add another layer of value. Arborists often mark up images to highlight specific concerns—circling areas of decay, drawing arrows to structural weaknesses, or outlining zones of concern. These visual aids help non-technical readers understand complex arboricultural issues quickly. Check out more about how much does emergency tree removal cost in NSW?
How Is Risk Assessment Conducted Regarding Trees on Property?
Tree risk assessment Sydney professionals use systematic evaluation methods to identify potential dangers trees may pose to people, structures, and surrounding property. The arborist examines each tree’s likelihood of failure and the potential consequences if failure occurs, creating a comprehensive risk profile that informs management decisions.
The assessment begins with evaluating the tree’s proximity to high-traffic areas, buildings, power lines, and other critical infrastructure. A large eucalyptus overhanging a children’s playground presents a different risk profile than an identical tree in an isolated corner of a rural property. The arborist documents these spatial relationships to determine the target zone—the area that could be affected if the tree or its parts were to fail.
Factors Influencing Structural Stability
Property risk evaluation trees considers multiple physical factors that influence structural stability:
- Tree size and age: Mature trees with extensive canopies create greater potential impact zones, while older specimens may have hidden decay
- Root system condition: Compromised root plates, soil compaction, or recent excavation work can destabilize even healthy-looking trees
- Trunk integrity: Cavities, cracks, splits, or fungal fruiting bodies indicate internal decay that weakens structural capacity
- Branch architecture: Included bark, co-dominant stems, or poor branch attachments increase likelihood of limb failure
- Lean angle: Trees leaning significantly toward targets require careful assessment of root anchorage and compensatory growth patterns
Environmental Factors Affecting Risk
Environmental context shapes risk calculations. Trees exposed to strong prevailing winds, located on slopes, or growing in shallow soils face different stress factors than sheltered specimens in deep, well-drained ground. Recent weather events, construction activities, or changes in site drainage can rapidly alter a tree’s risk profile.
Assigning Risk Ratings
The arborist assigns risk ratings using standardized frameworks such as the International Society of Arboriculture’s risk assessment methodology. These ratings typically categorize trees as low, moderate, high, or extreme risk based on the probability of failure combined with the potential for harm. A tree with significant defects but no nearby targets might receive a lower risk rating than a healthier tree positioned directly over a dwelling.
Recommendations Based on Risk Levels
Recommendations flow directly from identified risk levels. Low-risk trees may require only routine monitoring during periodic inspections. Moderate-risk situations often
What Legal and Council Documentation Is Included in the Report?
A comprehensive arborist report includes formal components specifically formatted for submission to local councils and legal entities. These documents serve as official records that satisfy regulatory requirements and support various applications involving tree management activities.
The report prepares documents that align with specific local government area requirements. Each Sydney council has distinct documentation standards, and qualified arborists structure their reports to meet these varying specifications. The documentation typically includes:
- Detailed tree inventory with precise location mapping
- Assessment summaries formatted for council review processes
- Compliance statements referencing relevant legislation
- Professional recommendations with supporting technical data
- Arborist credentials and certification details
Development applications requiring tree removal, pruning, or protection measures rely on these formal documents. Property owners seeking DA approval must submit arborist reports that demonstrate compliance with tree preservation orders and development control plans. The report provides councils with the technical justification needed to assess applications objectively.
Statutory requirements dictate specific information that must appear in council submissions. Reports include references to the Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016, local tree preservation orders, and relevant Australian Standards (AS 4970-2009 for tree risk assessment). This legal framework ensures the documentation holds weight in formal proceedings.
The arborist’s professional indemnity insurance details and qualifications appear prominently, establishing the report’s credibility for legal purposes. Courts and tribunals accept properly prepared arborist reports as expert evidence when disputes arise regarding tree management decisions.
Tree protection zone calculations, root zone assessments, and impact statements form part of the legal documentation package. These technical components support applications for construction near significant trees or within heritage conservation areas. The precision of this documentation often determines whether councils approve or reject development proposals.
How Long Does It Typically Take to Receive a Comprehensive Arborist Report in Sydney?
Most arborist reports in Sydney are delivered within 3 to 7 business days after the onsite inspection is completed. The arborist report turnaround time Sydney depends on the scope of assessment and the number of trees requiring evaluation.
Standard Report Delivery Timeframe
Simple assessments involving one or two trees typically arrive within 3 to 5 business days. The arborist conducts the inspection, analyzes findings, compiles photographic evidence, and prepares the formal documentation during this period.
Properties with multiple trees or complex site conditions may extend the report delivery timeframe to 7 business days or longer. Each additional tree requires individual assessment, documentation, and risk evaluation, which naturally increases preparation time.
What Factors Influence Report Preparation Duration?
Project complexity significantly impacts how quickly you receive your report:
- Number of trees: Single tree assessments process faster than multi-tree properties
- Site accessibility: Difficult terrain or restricted access areas require additional inspection time
- Tree condition: Trees with extensive health issues or structural concerns need more detailed analysis
- Regulatory requirements: Development applications requiring specific council documentation may need additional research and formatting
Urgency requests can sometimes expedite delivery. Many arborist services in Sydney offer priority reporting for time-sensitive development applications or emergency situations, though this may incur additional fees.
Seasonal demand affects turnaround times during peak periods. Spring and early summer see increased requests for arborist reports as property owners prepare for construction projects and development applications.
Why Does Timely Report Delivery Matter?
Development application deadlines create pressure for prompt report delivery. Councils often require arborist reports as part of DA submissions, and missing deadlines can delay entire projects by weeks or months.
Property transactions frequently depend on tree assessments. Buyers and sellers need reports quickly to proceed with negotiations, building inspections, or contract conditions related to tree preservation or removal.
Insurance claims involving tree damage demand swift documentation. Delayed reports can complicate claims processing and extend resolution timeframes for property damage disputes.
Emergency situations require immediate assessment and reporting. Dangerous trees threatening structures or public safety may need same-day or next-day reporting
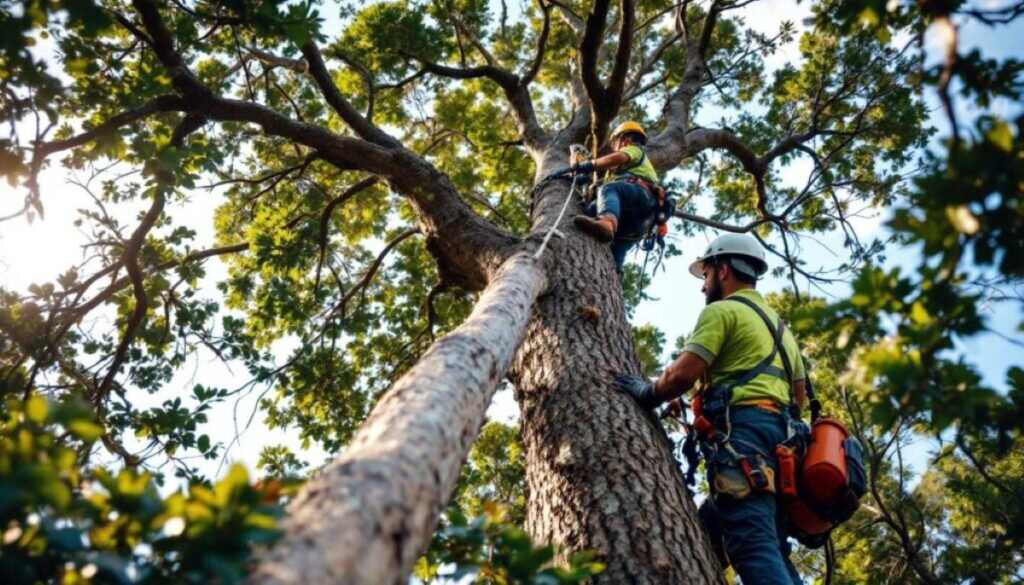

Conclusion
What Value Do Comprehensive Arborist Reports Provide to Property Stakeholders?
A comprehensive arborist report serves as an essential tool for responsible tree management across Sydney properties. These detailed assessments empower property owners, developers, and councils to make informed tree management decisions based on scientific evidence rather than guesswork.
The comprehensive arborist report benefits Sydney stakeholders experience include:
- Legal protection through documented compliance with local regulations
- Financial savings by identifying problems before they escalate into emergencies
- Safety assurance for residents, visitors, and neighbouring properties
- Environmental stewardship by preserving valuable trees where possible
- Streamlined approval processes for development applications
Property developers gain clarity on which trees require protection during construction, while homeowners receive actionable guidance for maintaining their landscape assets. Councils rely on these reports to make fair, evidence-based decisions about tree preservation orders and removal permits.
Why Should You Engage Qualified Arborists for Your Assessment?
The accuracy and reliability of your arborist report depends entirely on the expertise of the professional conducting it. Engaging arborists with AQF Level 5 certification ensures your assessment meets industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Qualified arborists bring:
- Technical knowledge to identify subtle signs of disease or structural failure
- Legal awareness of current Sydney council regulations and protected species
- Professional liability insurance for peace of mind
- Court-admissible documentation if disputes arise
When you understand What’s Included in a Comprehensive Arborist Report Sydney, you can better appreciate the depth of analysis required. This isn’t a simple visual check—it’s a thorough scientific evaluation that protects your interests and the urban forest.
Investing in a professional arborist report today prevents costly mistakes tomorrow, whether you’re planning renovations, purchasing property, or managing an existing landscape. The documentation becomes a valuable reference point for years of future tree care decisions.